Spares & Accessories
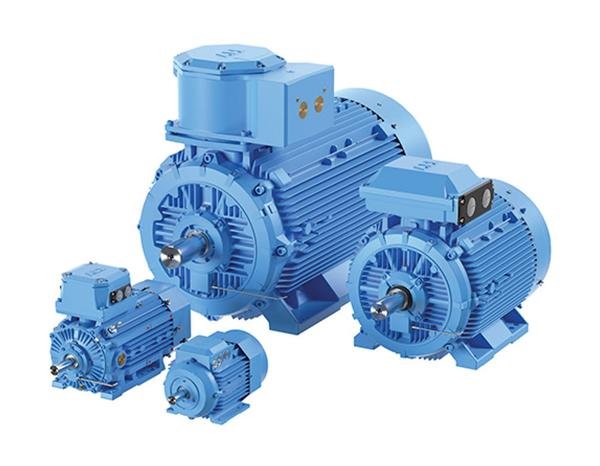
1. Electric Motors
- Safe Area Motors
- Super Premium Efficiency Motors – IE4
- Premium Efficiency Motors- IE3
- High Efficiency Motors – IE2
- Flameproof Motors
- Slip Ring Motors
- Textile Application Motors
- Crusher Duty Motors
- DC Motors




Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is a device that helps you in converting the fixed voltage and frequency of the input power provided to the motor, into variable voltage and frequency. This conversion regulates the functioning of your electric motor.
Majority of applications need variable speed during peak load and a constant speed when the load and current is normal. The key use of a VFD is to maintain the speed of a motor at a constant level even if there are disturbances in load and input.

Now that you are well-versed with the different types of VFDs and applications of the same, let us look at a few key features of the same.
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and HMI (Human-Machine Interface) are integral components of modern industrial automation systems. PLCs are programmable electronic devices used to control and automate various processes in manufacturing, such as machinery operation, production lines, and industrial processes. They are designed to monitor inputs from sensors and other devices, execute control algorithms, and generate outputs to control actuators and machinery.
On the other hand, HMIs are user interfaces that allow operators and technicians to interact with PLCs and other control systems. HMIs typically consist of graphical displays, touchscreens, and input devices such as buttons and switches. They provide real-time data visualization, control capabilities, alarm notifications, and system diagnostics, enabling users to monitor and manage industrial processes efficiently.
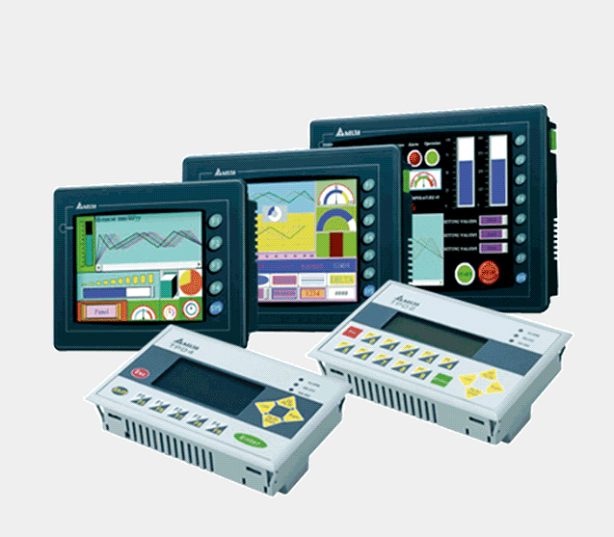

Together, PLCs and HMIs form the backbone of industrial automation, enabling seamless control, monitoring, and optimization of complex manufacturing processes while improving productivity, reliability, and safety.
An HMI is typically easier to use than a PLC because it has a graphical user interface that can be controlled with a mouse or touchscreen. This means that people without much knowledge of programming can still use a SCADA and HMI System to control machinery
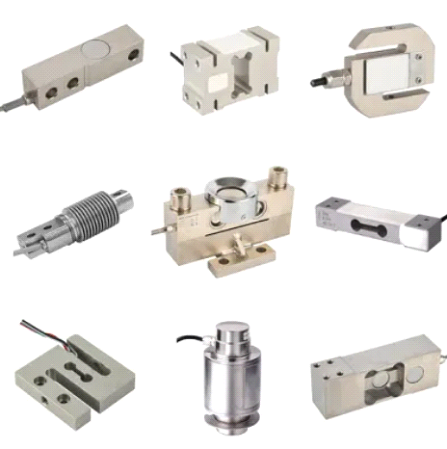
A load cell is a transducer used to convert mechanical force or weight into an electrical signal. It is commonly used in industrial applications to measure force, weight, or pressure. Load cells are essential components in various systems, such as weighing scales, industrial automation, material handling equipment, and testing machines.
Load cells work on the principle of strain gauge technology, where strain gauges are bonded to a metal structure that deforms under applied force. As the metal structure deforms, the strain gauges experience a change in resistance, which is converted into an electrical signal proportional to the applied force. This signal is then amplified and processed to obtain accurate measurements of the force or weight being applied.
There are different types of load cells available, including:
Load cells are calibrated to ensure accurate and reliable measurements. They are used in various industries such as manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and agriculture, where precise force or weight measurements are required for process control, quality assurance, and safety.
